|
|
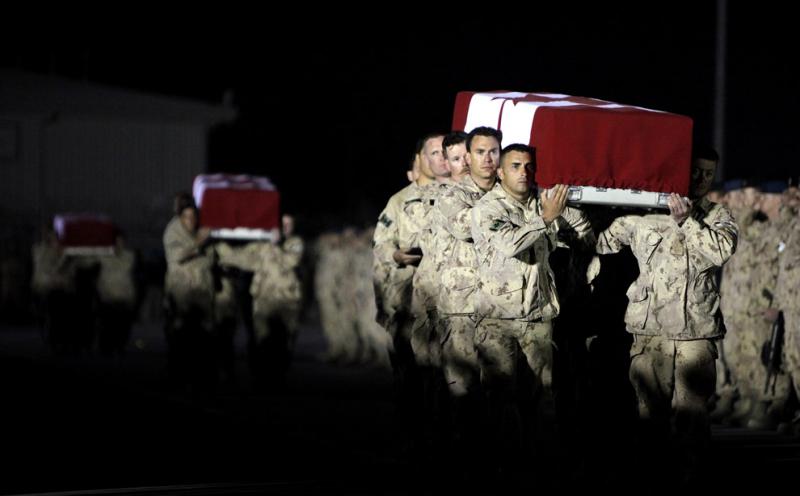
Life In Afghanistan
|
Afghanistan is variously described as being located within South Asia, Central Asia, and sometimes Western Asia (or the Middle East). Afghanistan is landlocked and mountainous, with plains in the north and southwest. The highest point is Nowshak, at 7,485 m (24,557 ft) above sea level. The climate varies by region and tends to change quite rapidly. Large parts of the country are dry, and fresh water supplies are limited. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world.
Afghanistan has a continental climate with very harsh winters in the central highlands, the glaciated northeast (around Nuristan) and the Wakhan Corridor, where the average temperature in January is below −15 °C (5.0 °F), and hot summers in the low-lying areas of Sistan Basin of the southwest, the Jalalabad basin of the east, and the Turkistan plains along the Amu River of the north, where temperature averages over 35 °C (95 °F) in July. The country is frequently subject to minor earthquakes, mainly in the northeast of Hindu Kush mountain areas. Some 125 villages were damaged and 4,000 people killed by the May 31, 1998 earthquake.
At 249,984 sq mi (647,456 km2), Afghanistan is the world's 41st-largest country (after Burma). The nation shares borders with Pakistan in the southeast, Iran in the west, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan in the north, and China in the far east. The country does not face any water shortage because it receives huge amount of snow during winter and once that melts the water runs into rivers, lakes, and streams, but most of its national water flows to neighboring states. The country needs around $2 billion to rehabilitate its irrigation systems so that the water is properly used.
|
|