|
|
History: Old Japan
|
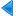
Tokugawa Ieyasu served as regent for Hideyoshi's son Toyotomi Hideyori, using his position to gain political and military support. When open war broke out, he defeated rival clans in the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600. Ieyasu was appointed shōgun in 1603 and established the Tokugawa shogunate at Edo (modern Tokyo). The Tokugawa shogunate enacted a variety of measures such as Buke shohatto to control the autonomous daimyo. In 1639, the shogunate began the isolationist sakoku ("closed country") policy that spanned the two and a half centuries of tenuous political unity known as the Edo period. The study of Western sciences, known as rangaku, continued during this period through contact with the Dutch enclave at Dejima in Nagasaki. The Edo period also gave rise to kokugaku ("national studies"), the study of Japan by the Japanese themselves. According to one authority, there were at least 130 famines during the Edo period, of which 21 were particularly serious.
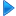
On March 31, 1854, Commodore Matthew Perry and the "Black Ships" of the United States Navy forced the opening of Japan to the outside world with the Convention of Kanagawa. Subsequent similar treaties with Western countries in the Bakumatsu period brought Japan into economic and political crises. The resignation of the shogunate led to the Boshin War and the establishment of a centralized state unified under the name of the Emperor (Meiji Restoration). Adopting Western political, judicial and military institutions, the Cabinet organized the Privy Council, introduced the Meiji Constitution, and assembled the Imperial Diet. The Meiji Restoration transformed the Empire of Japan into an industrialized world power that embarked on a number of military conflicts to expand the nation's sphere of influence. After victories in the First Sino-Japanese War (1894–1895) and the Russo-Japanese War (1904–1905), Japan gained control of Taiwan, Korea, and the southern half of Sakhalin. Japan's population grew from 35 million in 1873 to 70 million in 1935.
|
|