|
|
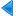
Child Miners, 20th Century, United States
|
Miners utilize equipment strong enough to break through extremely hard layers of the Earth's crust. This equipment, combined with the closed workspace that underground miners work in, can cause hearing loss. For example, a roof bolter (commonly used by mine roof bolter operators) can reach sound power levels of up to 115 dB. Combined with the reverberant effects of underground mines, a miner without proper hearing protection is at a high risk for hearing loss.
Since mining entails removing dirt and rock from its natural location creating large empty pits, rooms and tunnels, cave-ins are a major concern within mines. Modern techniques for timbering and bracing walls and ceilings within sub-surface mines have reduced the number of fatalities due to cave-ins, but accidents still occur. The presence of heavy equipment in confined spaces also poses a risk to miners, and despite modern improvements to safety practices, mining remains dangerous throughout the world.
Modern mines use automation and remote operation to improve the safety of mine workers. Examples include automated loaders and remotely operated rockbreakers.
|
|